Introduction to Cardiac Arrest in College Athletes
As an avid fan of sports and a health enthusiast, I've noticed a worrying trend: cardiac arrest among elite college athletes. While these young individuals are in the prime of their lives and the peak of their physical fitness, they are not immune to the dangers of sudden cardiac arrest. In this article, we'll explore the reasons behind this phenomenon and discuss ways to prevent it. Let's dive into the details and uncover the factors that contribute to this alarming occurrence.
The Pressure to Perform at a High Level
One of the main reasons why cardiac arrest is so common in elite college athletes is the immense pressure they face to perform at a high level. These young athletes are often under constant scrutiny from coaches, peers, and even the media. The pressure to excel in their sport can lead to overexertion, pushing their bodies beyond their limits, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrest.
Moreover, the intense training regimen and the stress of balancing academics and athletics can take a toll on their overall health. High levels of stress can contribute to an increased risk of heart problems, including sudden cardiac arrest. It's crucial for athletes to find ways to manage stress and maintain a healthy balance in their lives to reduce this risk.
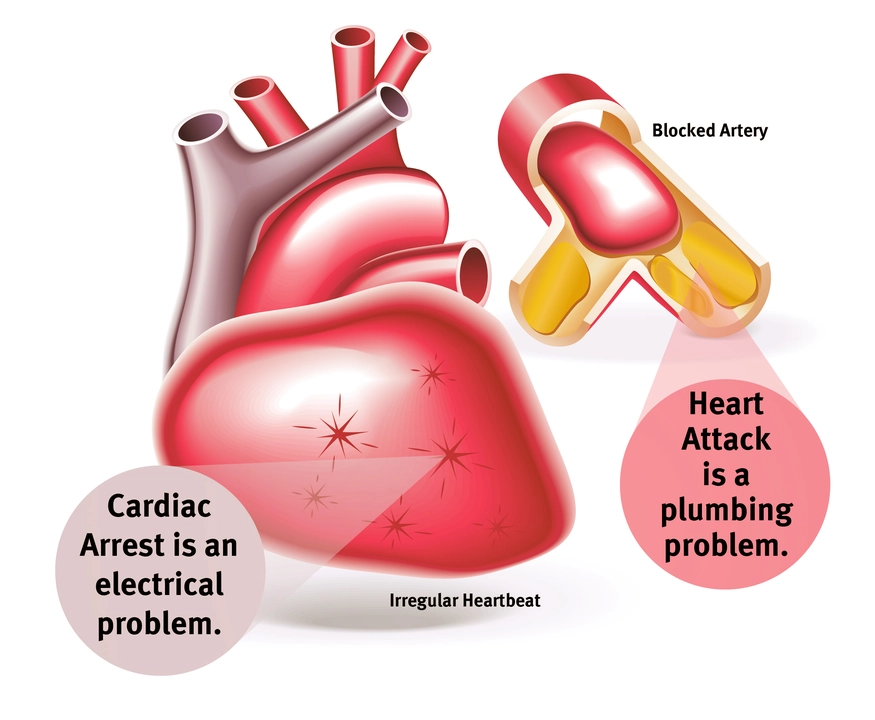
Undiagnosed Heart Conditions
Another factor contributing to the prevalence of cardiac arrest in elite college athletes is undiagnosed heart conditions. Many athletes may not be aware that they have a pre-existing heart condition, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or coronary artery anomalies. These conditions can remain asymptomatic until triggered by intense physical activity, leading to sudden cardiac arrest.
Regular heart screenings and comprehensive physical exams are essential for early detection and management of these conditions. Athletes should also be vigilant about reporting any unusual symptoms, such as chest pain or shortness of breath, to their healthcare providers.
Use of Performance-Enhancing Drugs
Unfortunately, the use of performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs) is not uncommon among elite college athletes. These substances can significantly increase the risk of cardiac arrest, as they can lead to an enlarged heart, irregular heart rhythms, and increased blood pressure. Furthermore, PEDs can mask the symptoms of underlying heart conditions, making it even more challenging to diagnose and treat them before it's too late.
Educating athletes about the dangers of PEDs and promoting a culture of fair play and drug-free competition can help reduce the risk of cardiac arrest stemming from their use.
Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances can also contribute to an increased risk of cardiac arrest in elite college athletes. During intense physical activity, athletes lose fluids and essential electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, through sweat. These electrolytes play a critical role in maintaining proper heart function and muscle contraction. If not adequately replenished, an electrolyte imbalance can lead to abnormal heart rhythms and, in severe cases, cardiac arrest.
To prevent this, athletes should focus on staying well-hydrated and replenishing lost electrolytes through sports drinks or electrolyte supplements.
Inadequate Recovery and Overtraining
Overtraining and inadequate recovery can also increase the risk of cardiac arrest in elite college athletes. Pushing the body to its limits without allowing sufficient time for rest and recovery can cause physical and mental stress, which can negatively impact heart health. Over time, chronic overtraining can lead to a weakened immune system, hormonal imbalances, and increased inflammation, all of which can contribute to an increased risk of cardiac arrest.
To avoid overtraining, athletes should prioritize rest and recovery, listen to their bodies, and work with their coaches to develop a balanced training program that promotes long-term health and performance.
Improper Warm-Up and Cool-Down Procedures
Skipping proper warm-up and cool-down procedures can also contribute to an increased risk of cardiac arrest in elite college athletes. A thorough warm-up prepares the heart and muscles for intense activity, while a proper cool-down helps return the heart rate to normal and facilitates recovery.
By neglecting these essential components of a workout, athletes may be putting added stress on their hearts, increasing the risk of cardiac arrest. Therefore, it's crucial to incorporate adequate warm-up and cool-down periods into every training session.
The Role of Genetics
Genetics can also play a role in the risk of cardiac arrest among elite college athletes. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to heart conditions, making them more susceptible to cardiac arrest. In some cases, these genetic factors can remain undetected until a triggering event, such as intense physical activity, occurs.
While genetic factors may be beyond our control, being aware of family history and discussing any concerns with healthcare providers can help athletes take proactive steps to monitor and manage their heart health.
Importance of Emergency Action Plans
Having an emergency action plan (EAP) in place is crucial to increasing the chances of survival in the event of a cardiac arrest. An EAP should include the availability of an automated external defibrillator (AED), a designated emergency response team, and a clear communication plan for dealing with cardiac emergencies.
By being prepared and knowing how to respond quickly and effectively, we can help save the lives of young athletes who may suffer from sudden cardiac arrest.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Heart Health in College Athletics
Cardiac arrest is an unfortunate reality for many elite college athletes, but it doesn't have to be. By understanding the risks and taking proactive steps to prioritize heart health, we can help protect these young athletes and ensure they can continue to pursue their passion for sports safely. Let's work together to raise awareness of this issue and promote a culture of health and well-being in college athletics.